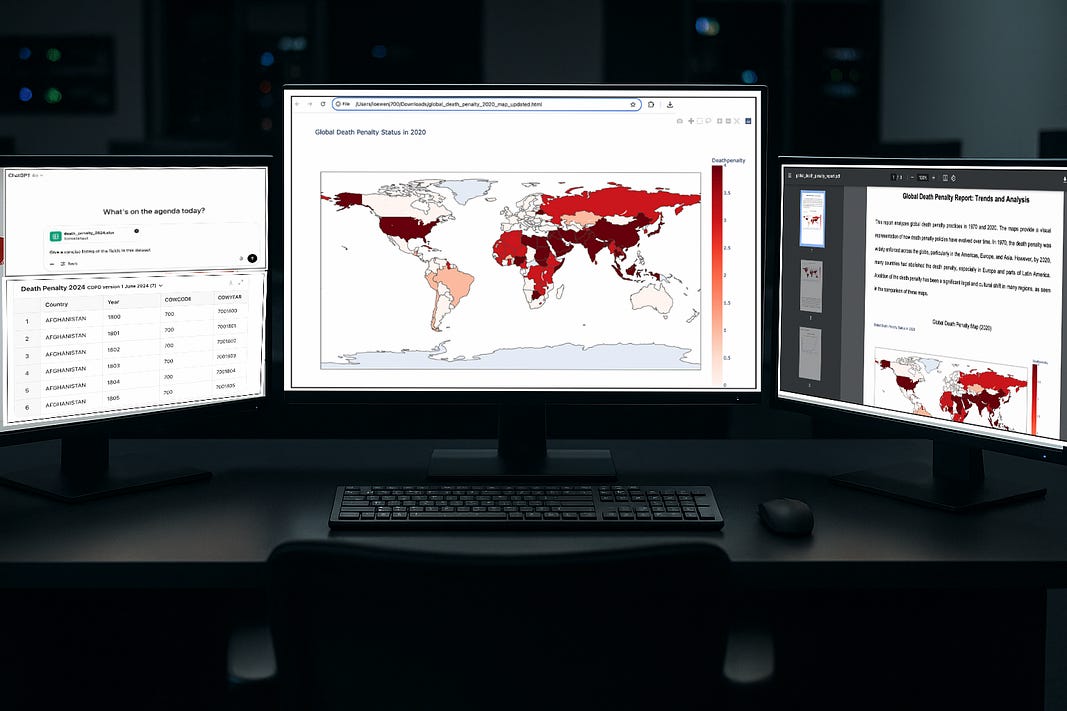
Is GPT-4o Now Any Better With Data Visualization Report Creation?
Testing GPT-4o data viz automatic PDF report generation using a UN dataset
GPT-4o, as one of the most powerful large language models, can analyze data, generate data visuals, and create PDF reports from complex datasets.
For example, you can ask the LLM to access and provide information about each data field in your spreadsheet files and it will respond quickly and accurately.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Data at Depth to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.